Architecture
Now let's discuss how the architecture of our solution will look like. It will be a little different from the RTMP to HLS architecture. In most cases communication with a RTSP server is split into two phases:
- Negotiation of the stream parameters over RTSP.
- Receiving RTP stream(s) that the client and server have agreed upon.
Both of these phases are handled by RTSP Source. Let's take a closer look how each of them folds out:
Establishing the connection
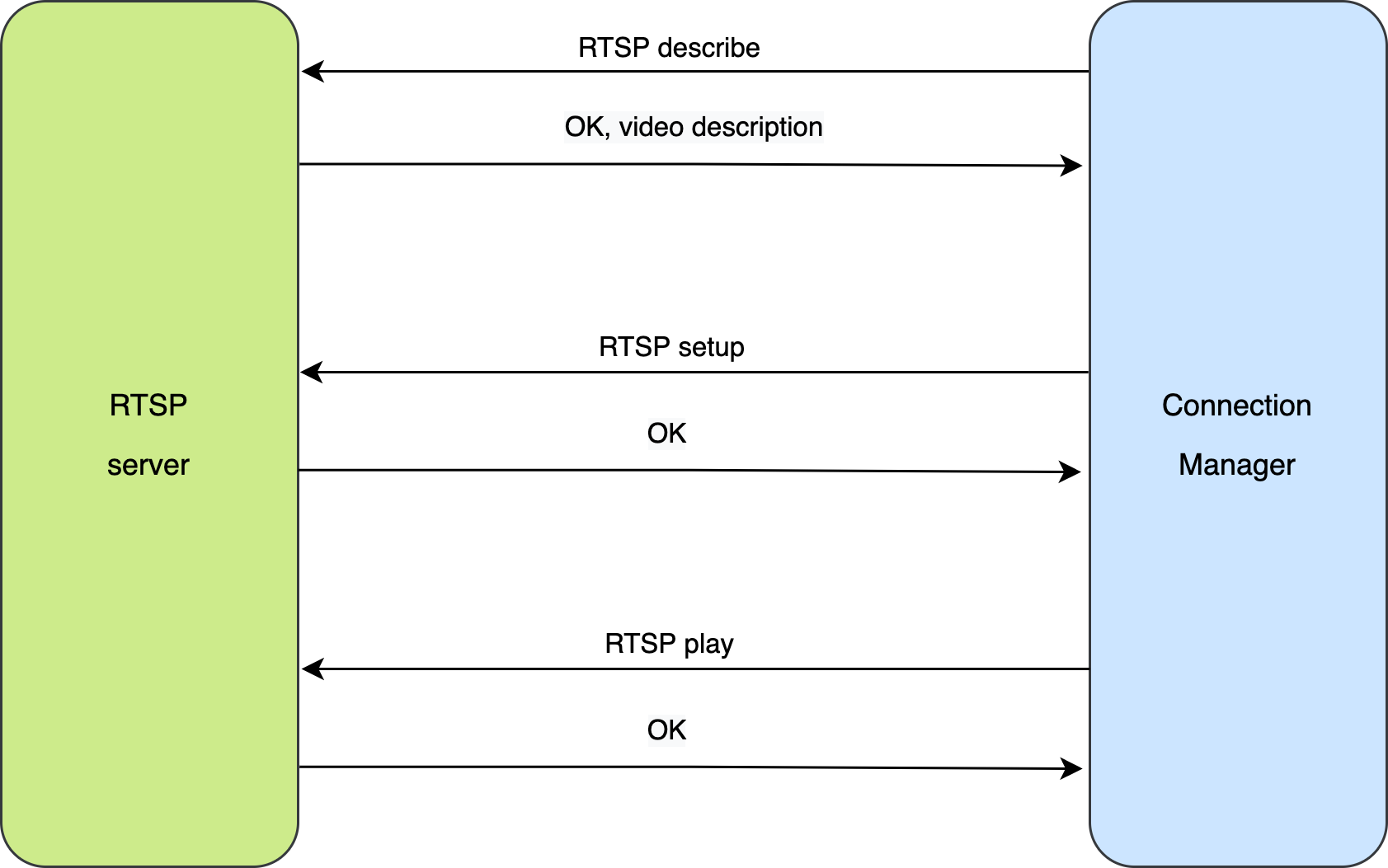
When establishing a connection the source will act as a connection manager, initializing the RTSP session and starting the stream playback. It communicates with the server using the RTSP requests. In fact, we won't need many requests to start playing the stream - take a look at the desired message flow:
First we want to get the details of the video we will be playing, by sending the DESCRIBE method.
Then we call the SETUP method, defining the transport protocol (RTP) and client port used for receiving the stream.
Now we can start the stream using PLAY method.
Receiving the stream
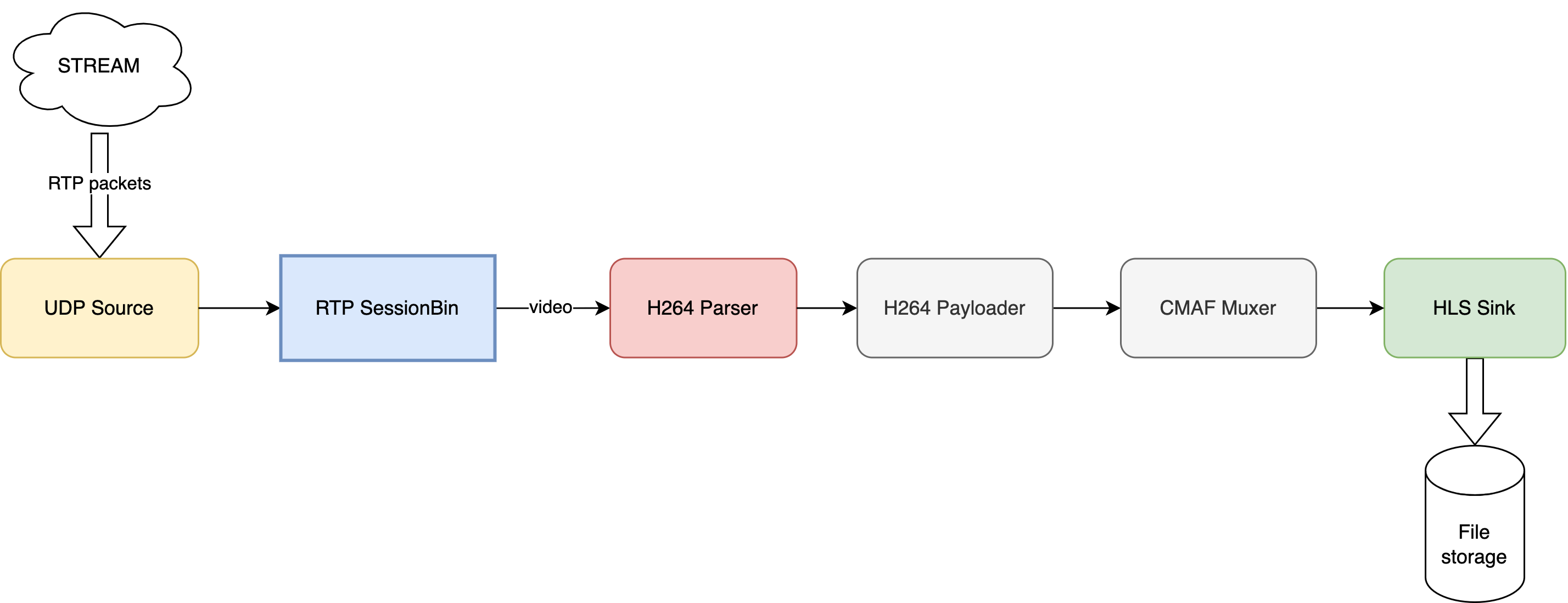
The source is a bin containing a few elements, each of them performing a specific media processing task. You can definitely notice some similarities to the pipeline described in the RTMP architecture. However, we will only be processing video so only the video processing elements will be necessary.
We have already used the H264 Parser and HLS Sink Bin elements in the RTMP pipeline, take a look at the RTMP to HLS architecture chapter for details of the purpose of those elements.
Let us describe briefly what is the purpose of the other components:
UDP Source
This element is quite simple - it receives UDP packets from the network and sends their payloads to the next element.
RTP Demuxer
This element is responsible for getting media packets out of the RTP packets they were transported in and routing them according to their SSRC. In our case we only receive a single video stream, so only one output will be used.
RTP H264 Depayloader
When transporting H264 streams over RTP they need to be split into chunks and have some additional metadata included. This element's role is to unpack the RTP packets it receives from the Demuxer into a pure H264 stream that can be processed further.