Bin
A Membrane's bin is a container for elements, which allows for creating reusable groups of elements. Bin is similar to a pipeline in that it consists of linked elements. Such bin can then be placed inside a pipeline and linked with other entities - elements or bins. Bins can also be nested within one another. Bin also has another advantage - it manages its children, for instance by dynamically spawning or replacing them as the stream changes.
Enclosing pipeline elements inside a bin
As you can see, we have Source -> Ordering Buffer -> Depayloader chain, which is duplicated.
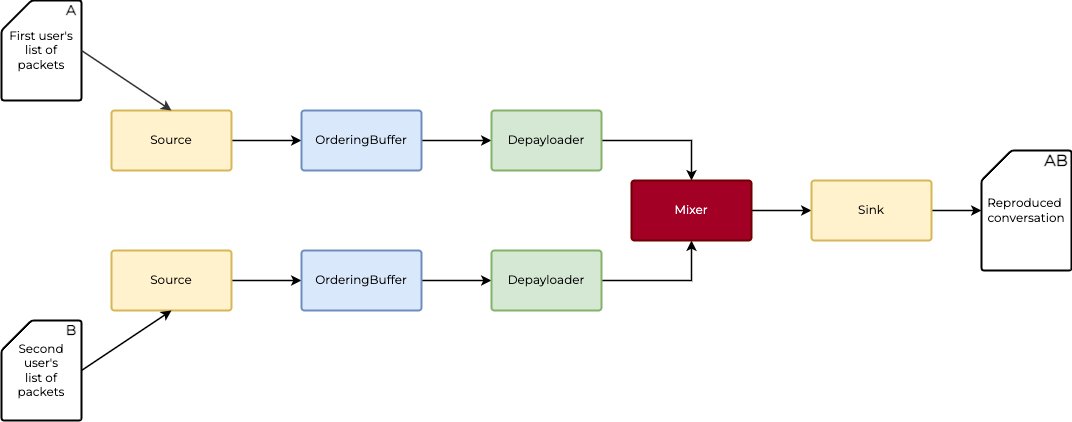
We can encapsulate these elements inside Bin.
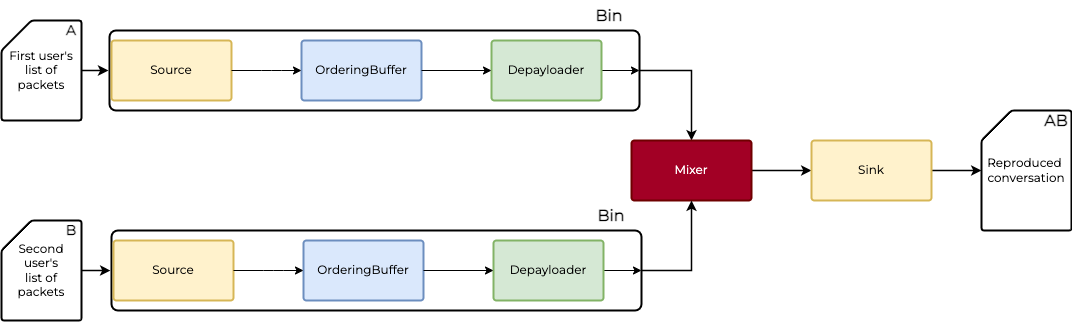
Notice that there is no direct connection between Depayloader and Mixer. We have to explicitly link the Depayloader with Bin's output pads and then we will connect the output pads to Mixer's input pads.
Let's define the bin's output pads and its elements.
lib/Bin.ex
defmodule Basic.Bin do use Membrane.Bin def_output_pad :output, accepted_format: %Basic.Formats.Frame{encoding: :utf8} def_options input_filename: [ type: :string, description: "Input file for conversation." ] @impl true def handle_init(_ctx, options) do spec = [ child(:input, %Basic.Elements.Source{location: options.input_filename}) |> child(:ordering_buffer, Basic.Elements.OrderingBuffer) |> child(:depayloader, %Basic.Elements.Depayloader{packets_per_frame: 4}) |> bin_output(:output) ] {[spec: spec] %{} } end end
The output pads of the bin are matching the ones we defined for depayloader.
Notice that the last link is between depayloader and the bin's output pads. In general, if we wanted to receive data in a bin we would need to link the first processing component in the bin with the bin_input(<bin's input pad name>).
Modifying pipeline using bin
Using the bin we created, we can replace the elements in the pipeline.
lib/Pipeline.ex
defmodule Basic.Pipeline do @moduledoc """ A module providing the pipeline, which aggregates and links the elements. """ use Membrane.Pipeline @impl true def handle_init(_ctx, _opts) do spec = [ child(:bin1, %Basic.Bin{input_filename: "input.A.txt"}) |> via_in(:first_input) |> child(:mixer, Basic.Elements.Mixer), child(:bin2, %Basic.Bin{input_filename: "input.B.txt"}) |> via_in(:second_input) |> get_child(:mixer), get_child(:mixer) |> child(:output, %Basic.Elements.Sink{location: "output.txt"}) ] {[spec: spec], %{}} end end
Combining the usage of the bin and dynamic pads will result in an even cleaner and more scalable solution.